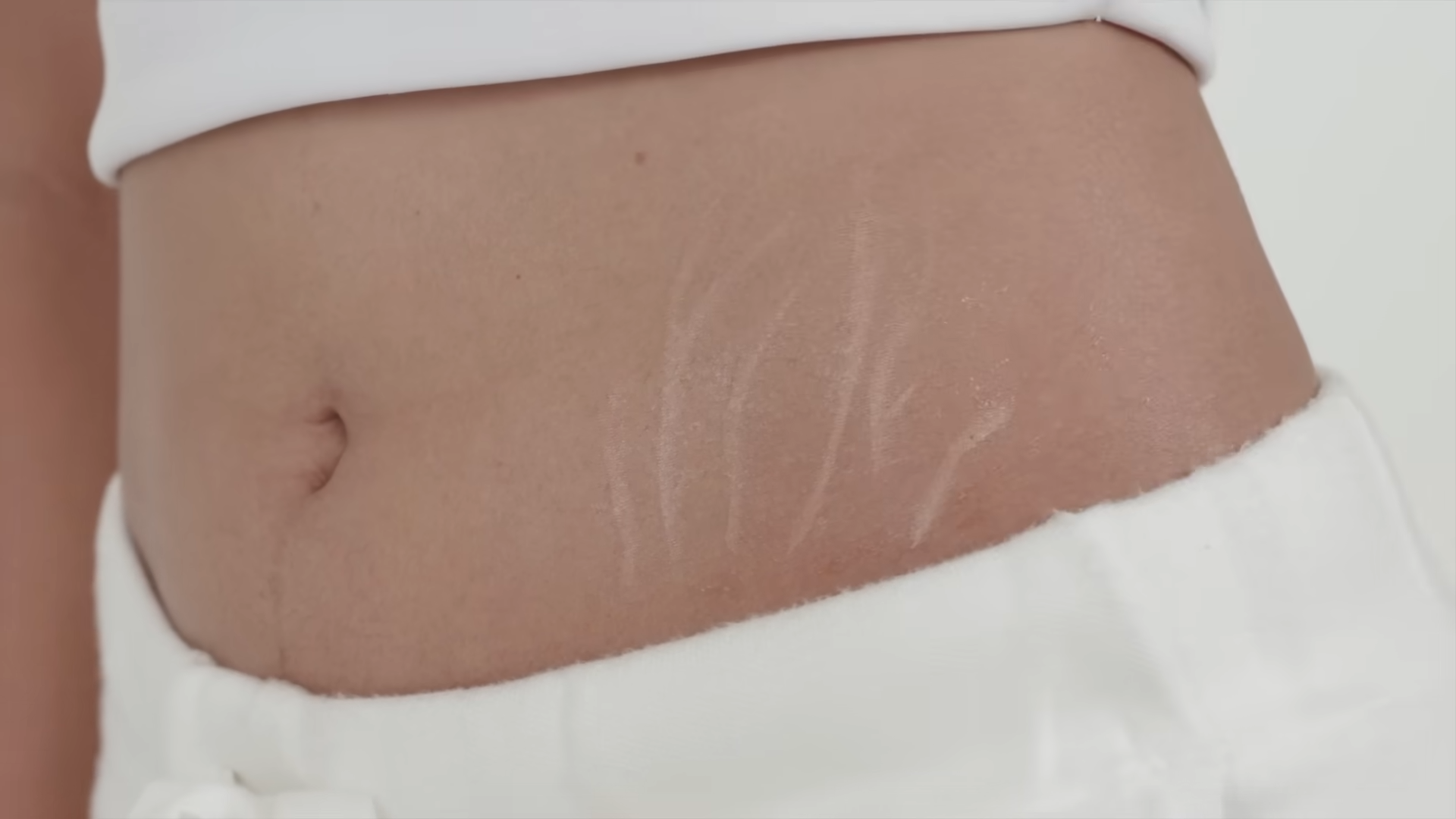
Stretch marks, medically known as striae distensae, are a common concern affecting both men and women, often appearing on areas prone to rapid skin stretching such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, and breasts. These marks develop when the skin stretches beyond its natural elasticity, causing the collagen and elastin fibers to rupture. Pregnancy, rapid weight gain or loss, puberty, and certain medical conditions like Cushing’s syndrome can contribute to their formation. Understanding the causes is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Preventing stretch marks involves maintaining skin elasticity through hydration and proper nutrition. Regularly moisturizing the skin with creams or oils rich in vitamins A and E can improve skin elasticity and resilience. During pregnancy or periods of rapid weight change, gradually increasing weight and staying within recommended gain limits can minimize stretch marks. When treating existing stretch marks, options include topical treatments containing retinoids or hyaluronic acid to promote collagen production and improve skin texture. Laser therapy and microdermabrasion are also effective in reducing the appearance of older, more established stretch marks by stimulating skin regeneration.
To understand how to prevent and treat stretch marks effectively, it’s essential to explore their causes and the best solutions available. The following subheadings will delve into the causes of stretch marks, prevention strategies, and treatment options.
To understand how to prevent and treat stretch marks effectively, it’s essential to explore their causes and the best solutions available. The following subheadings will delve into the causes of stretch marks, prevention strategies, and treatment options.
Causes of Stretch Marks
Stretch marks are a common skin condition characterized by visible streaks or lines that form when the skin undergoes rapid stretching. This stretching exceeds the skin’s natural elasticity, causing the underlying collagen and elastin fibers to tear. The most common causes of stretch marks include significant weight fluctuations, such as rapid weight gain or loss, which can occur during pregnancy or puberty. These periods of rapid growth or changes in body shape put immense strain on the skin, leading to the formation of stretch marks. Additionally, medical conditions like Cushing’s syndrome, which involve increased levels of cortisol, can weaken the skin’s structural integrity, further predisposing it to developing stretch marks. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and manage stretch marks.
Addressing stretch marks begins with proactive prevention strategies aimed at maintaining skin elasticity and resilience. For individuals prone to stretch marks due to pregnancy or rapid weight changes, gradual weight management and staying within recommended gain limits can minimize their occurrence. Keeping the skin well-hydrated with moisturizers containing vitamins A and E helps improve its ability to stretch without tearing. Furthermore, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients like zinc, vitamin C, and protein supports skin health and elasticity. By understanding the factors that contribute to stretch marks and implementing preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk and manage the appearance of existing stretch marks effectively.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing stretch marks involves proactive measures to maintain skin elasticity and resilience. Hydration plays a crucial role, as regularly moisturizing the skin with creams or oils containing vitamins A and E helps improve its ability to stretch without tearing. These nutrients nourish the skin, enhancing its natural elasticity and reducing the likelihood of developing stretch marks. During pregnancy or periods of rapid weight change, gradual weight management is essential. Staying within recommended gain limits helps minimize the strain on the skin and reduces the risk of stretch marks forming.
In addition to hydration, nutrition plays a vital role in preventing stretch marks. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and essential nutrients supports overall skin health. Consuming foods high in zinc, vitamin C, and protein promotes collagen production and strengthens the skin’s structure, making it more resilient to stretching. By adopting these preventive measures—maintaining proper hydration, managing weight gain gradually, and following a nutritious diet—individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing stretch marks during periods of rapid growth or weight fluctuation.
Treatment Options
Treating existing stretch marks involves employing diverse methods aimed at enhancing skin texture and reducing their visibility. Topical treatments containing ingredients like retinoids or hyaluronic acid are effective for newer stretch marks. These substances work by stimulating collagen production, which helps to improve skin elasticity and fade the appearance of stretch marks over time.
For older and more established stretch marks, advanced treatments such as laser therapy and microdermabrasion are highly beneficial. Laser therapy targets the affected areas with focused light beams to stimulate the production of new collagen and elastin fibers. This process gradually improves the texture and color of stretch marks, making them less noticeable. Similarly, microdermabrasion mechanically exfoliates the skin’s outer layer, encouraging the growth of new, healthier skin cells. Both treatments promote skin regeneration and can significantly reduce the appearance of even stubborn stretch marks, enhancing skin appearance and boosting self-confidence.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing Stretch Marks
Understanding the causes of stretch marks is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Stretch marks, medically known as striae distensae, develop when the skin stretches beyond its natural elasticity, causing collagen and elastin fibers to rupture. Factors such as rapid weight gain or loss, pregnancy, puberty, and medical conditions like Cushing’s syndrome contribute to their formation. By comprehending these underlying causes, individuals can adopt proactive measures to prevent stretch marks and effectively manage their appearance.
Preventing stretch marks begins with maintaining skin elasticity through hydration and proper nutrition. Regularly moisturizing the skin with creams or oils rich in vitamins A and E enhances its ability to stretch without tearing. Gradual weight management during pregnancy or periods of rapid growth helps minimize skin strain and reduces the likelihood of stretch marks. For existing stretch marks, treatments such as topical retinoids or hyaluronic acid promote collagen production, improving skin texture and reducing their visibility over time. Advanced options like laser therapy and microdermabrasion further stimulate skin regeneration, offering effective solutions for managing stretch marks of varying severity.
By addressing the causes of stretch marks and implementing preventive measures and treatments tailored to individual needs, individuals can significantly reduce their impact and enhance skin health. Understanding these strategies empowers individuals to maintain smooth, resilient skin and boost confidence in their appearance.